Nucleosides & Nucleotides
Biochemicals
Nucleosides & Nucleotides
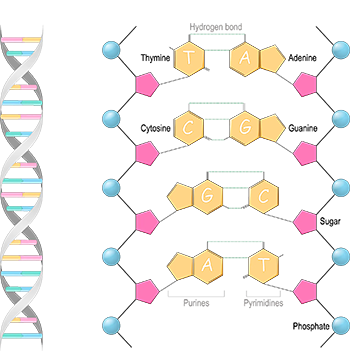
Nucleosides and nucleotides and their derivatives are biologically ubiquitous substances that participate in nearly all biochemical processes. They form the monomeric units of nucleic acids and thereby play central roles in both the expression and storage of genetic information.
Nucleosides are glycosylamines obtained by chemical or enzymatic decomposition of nucleic acids and contain two components: a five-carbon sugar (ribose or 2’ deoxyribose) and a nitrogen base. The nitrogenous bases are planar, aromatic, heterocyclic molecules. For the most part, are derivatives of purine or pyrimidine. The major purine components of nucleic acids are adenine (A) and guanine (G) residues and the major pyrimidine residues are cytosine (C), Uracil (U) (which mainly occurs in RNA), and thymine1. In double-helical DNAs and RNAs, the base compositions obey Chargaff’s rules: A=T(U) and G=C1. Examples of nucleosides include adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, uridine, and deoxythymidine. They function as signaling molecules and are precursors for nucleotides needed for DNA and RNA synthesis. Nucleosides also play a vital role in medicine and molecular biology and are used as antiviral or anticancer agents1.
As the building block of RNA and DNA, nucleotides are organic molecules composed of three components: a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogen base and, one or more phosphate groups. The nitrogen bases in the great majority of nucleotides are the purines (Adenine + Guanine) and the pyrimidines (Cytosine, either Thymine in DNA or Uracil in RNA). Examples of nucleotides include Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), Guanosine monophosphate (GMP), Cytidine monophosphate (CMP), Uridine monophosphate (UMP), and Deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP)1. Nucleotides are not only the basic unit of genetic material in all living things, but they also play a role in the energy, metabolism, and signaling in cells. In addition to their biological functions, nucleotides, and their derivatives play an important role in medical applications. By using the synthetic purine and pyrimidine analogs that contain halogens, thiols, or additional nitrogen atoms in the chemotherapy of cancer and AIDS, and immune suppressors during organ transplantation2.


